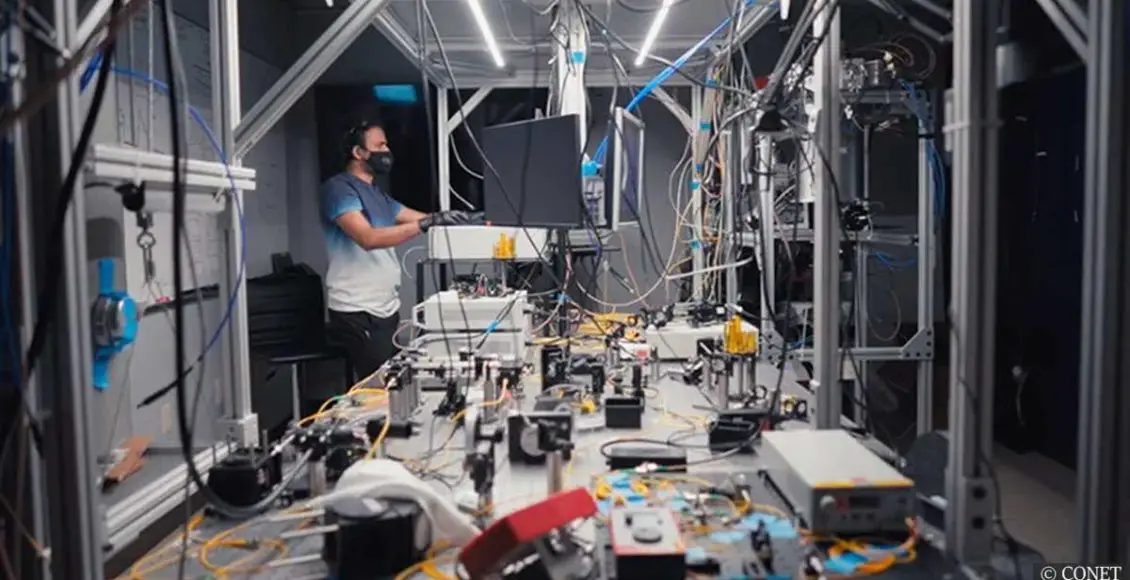
Major Breakthrough: Long-distance ‘quantum teleportation’ has been recently achieved by NASA scientists for the first time ever!
- Scientists achieved long-distance quantum teleportation.
- The experts state that quantum teleportation is faster than the speed of light.
- It could soon completely change our understanding of how computers work.
Quantum teleportation, the act of transferring quantum information from one location to another, is setting strong foundations for a quantum internet service. As per Daily Mail, it could one day revolutionize computing.
The unique aspect that makes quantum communication systems better than regular networks is that they use photons rather than computer code, which can be hacked. The leading-edge theory the scientists used entirely transforms our current understanding of how computers operate.
How does the quantum internet work?
The information in a quantum internet is stored in qubits – the quantum equivalent of computer bits. It is then ‘teleported’ from one location to another through a process called entanglement. During this process, two particles are linked, so that information shared with one is shared with the other at exactly the same time.
Therefore, the quantum state of each particle is dependent on the state of the other, regardless of the distance between them. In other words, quantum teleportation is the transfer of quantum states over long distances.
Researchers from Caltech, NASA, and Fermilab made quantum teleportation possible.
Although the process is highly sensitive and technologically challenging, the scientists managed to build an ingenious system between two labs separated by 27 miles (44km). It includes three nodes that interact with one another. While interacting, they trigger a sequence of qubits, which pass a signal from one place to the other instantly.
According to the brand new study published in PRX Quantum, the teleportation is faster than the speed of light with a fidelity of 90%. Fidelity measures how close the resulting qubit signal is to the original message.

Professor Maria Spiropulu from Caltech explains:
“This high fidelity is important especially in the case of quantum networks designed to connect advanced quantum devices, including quantum sensors.”
Plans of how policy-makers will use this cutting-edge technology are already circulating.
The US Department of Energy for example has plans to construct a quantum network between its laboratories across the country. However, there is still plenty of work and research to be done before employing quantum teleportation in our everyday lives.
What the experts predict is that the power of a quantum computer running on quantum internet will exceed the speeds of the world’s current most advanced supercomputers by around 100 trillion times.

Panagiotis Spentzouris, head of the Quantum Science Program at Fermilab, told Motherboard:
“There are many fronts that we need to push forward both in applications of quantum communication and network technologies and in advancing the engineering of the systems. We are already working hard on developing architecture, processes, and protocols for quantum networks and on optimizing along some metrics including rate of communications and range.”



